Search results
Search for "DNA binding" in Full Text gives 56 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Photoinduced in situ generation of DNA-targeting ligands: DNA-binding and DNA-photodamaging properties of benzo[c]quinolizinium ions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 101–117, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.11
- irradiation of the styrylpyridines and formation of the intercalator directly in the presence of DNA. In addition to the DNA-binding properties, the tested benzo[c]quinolizinium derivatives also operate as photosensitizers, which induce DNA damage at relative low concentrations and short irradiation times
- intercalators, and some currently applied anticancer drugs actually operate on the basis of intercalation [3]. Hence, several classes of compounds have been established, whose DNA-binding properties can be tailored and fine-tuned for that purpose, for example anthracyclines [5], indolocarbazoles [6], acridines
- [7], quinoxalines [8], naphthalimides [9], phenanthridines [10], cyanines [11], or indoles [12], as well as metal-organic complexes [13], and several others [1][2][4]. In this context, benzoquinolizinium derivatives and resembling polycyclic azoniahetarenes are an established class of DNA-binding
Synthesis and biological evaluation of Argemone mexicana-inspired antimicrobials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1511–1524, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.108
- ) protein [16][17], as well as perturbing carbohydrate metabolism to generate reactive oxygen species that damage the DNA [18], as modes of action for berberine’s antibacterial effects. The antitumor properties of berberine have been attributed to DNA binding, and in particular regulating the activity of
Synthesis of phenanthridines via a novel photochemically-mediated cyclization and application to the synthesis of triphaeridine
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2340–2347, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.152
- captivated synthetic chemists and biologists alike since the 1960s due to their efficient DNA binding, antitumour and antiparasitic activities [1]. Such compounds include the DNA and RNA-fluorescent marker ethidium bromide (1), the cell viability probe propidium iodide (2) and the naturally occurring
Cationic oligonucleotide derivatives and conjugates: A favorable approach for enhanced DNA and RNA targeting oligonucleotides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1828–1848, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.125
- injected before the plasmid, and no inhibition could be observed when the plasmid was injected first. This indicated that a competition between the cationic TFOs and the histones for DNA binding had a large impact [111]. The library of phosphoramidate variants was expanded when the aminobutyl
A systems-based framework to computationally describe putative transcription factors and signaling pathways regulating glycan biosynthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1712–1724, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.119

- their tissue-specific expression, DNA binding domains, and nucleosome interaction sequences [3]. Additional factors regulating transcriptional activity include: i) cofactors and small molecules that enable TF-DNA recognition and RNA polymerase recruitment [3]; ii) chromatin modifications, such as
Chemical approaches to discover the full potential of peptide nucleic acids in biomedical applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1641–1688, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.116
- favorable for DNA binding [60]. At the time of this writing, binding of S,S-cpPNA to complementary RNA remains less well explored; however, other constrained backbone-modified PNAs reviewed above have shown stronger binding to RNA over DNA. S,S-cpPNA may be expected to follow this trend and, at this time
- dichroism studies showed that the ᴅ-Lys modification induced a right-handed helical conformation favorable for DNA binding while the ʟ-Lys modification induced a left‐handed helical conformation that disfavored PNA binding to DNA [69]. Interestingly, a crystal structure of PNA having three α-ᴅ-Lys
Synthesis of 10-O-aryl-substituted berberine derivatives by Chan–Evans–Lam coupling and investigation of their DNA-binding properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 991–1000, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.81
- functionality. Thus, this synthetic route represents the first successful Cu-mediated coupling reaction of berberine substrates. The DNA-binding properties of the 10-O-arylberberine derivatives with duplex and quadruplex DNA were studied by thermal DNA denaturation experiments, spectrometric titrations as well
- , it has been found that berberine (1a) exhibits a selective cytotoxicity against cancer cells [12][13], which is mainly based on its DNA-binding properties [14]. Since the complexation with DNA leads to significant changes of the fluorescent quantum yields of the bound berberine, it can also be used
- berberrubine. And herein, we report the application of this Cu-mediated coupling reaction for the synthesis of 10-O-arylated berberine derivatives as unexpected reaction product, along with first experiments that demonstrate the G4-DNA-binding properties of this class of berberine derivatives. Results and
Au(III) complexes with tetradentate-cyclam-based ligands
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 186–192, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.18
- ][20][21]. Simple [Au(III)–cyclam] complexes have been investigated for various biological properties [22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29]. Particularly, studies have focused on their potential in vitro anticancer properties [24][26][29], the activity against a falciparum strain [22], the in vitro DNA
- binding properties [25] and reactions with bovine serum albumin [27]. Cyclam is known as a tetraamino-macrocyclic ligand, which binds strongly to give complexes with many transition metal cations. While catalytic applications of square planar cyclam complexes are reported for metals, such as Ni [30][31
Synthesis and investigation of quadruplex-DNA-binding, 9-O-substituted berberine derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2795–2806, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.230
- . DNA-binding properties Spectrometric titrations The interactions of the conjugates 4a–e with the quadruplex-forming oligonucleotides 22AG dA(G3TTA)3G3 and a2 d(ACAG4TGTG4)2 were analyzed by photometric and fluorimetric titrations (Figure 1). In all cases, the initial absorption maxima of the ligands
Naphthalene diimide bis-guanidinio-carbonyl-pyrrole as a pH-switchable threading DNA intercalator
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2201–2211, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.185

- not observe any emission, neither for single dye binding to DNA, nor in crowding conditions (excess of dye over DNA binding sites) at which eventually fluorescent excimers could be formed. Interactions with DNA/RNA Because of significant differences in the protonation states of compound 4, studies
Naphthalene diimide–amino acid conjugates as novel fluorimetric and CD probes for differentiation between ds-DNA and ds-RNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2032–2045, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.170
- pH control over DNA/RNA binding. There are several other systems also taking advantage of pH-controlled DNA binding [28], and such pH control could be further used also in selective antitumour strategies, taking advantage of many solid tumours having significantly lowered extracellular pH [29][30
A smart deoxyribozyme-based fluorescent sensor for in vitro detection of androgen receptor mRNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1135–1141, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.100

- the N-terminal domain (NTD). In vitro studies demonstrated that the progressive expansion of the length of the CAG repeat in NTD decreased its transactivation function. Exons 2 and 3 code the central DNA-binding domain and exons 4 to 8 code the C-terminal ligand-binding domain [14][15]. There are
Cation-induced ring-opening and oxidation reaction of photoreluctant spirooxazine–quinolizinium conjugates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 904–916, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.82

- been shown that derivatives thereof have a great potential to serve as functional units in DNA-binding ligands [54], fluorescent dyes and chemosensors [55][56][57][58][59]. Furthermore, we have already demonstrated that styryl-substituted quinolizinium derivatives exhibit ideal photophysical and DNA
- -binding properties to be used as DNA-sensitive fluorescent probes in cell imaging [60][61][62] or as photoswitchable DNA ligands [63]. Therefore, we were interested in a combination of the photochromic properties of the spirooxazine moiety with the advantageous photophysical and biological properties of
p-Pyridinyl oxime carbamates: synthesis, DNA binding, DNA photocleaving activity and theoretical photodegradation studies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 337–350, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.33

- DNA-photocleavers, and are proposed as new leads for “on demand” biotechnological applications in drug discovery and medicine. Keywords: DNA binding; DNA photocleavage; N–O homolysis; oxime carbamates; photocleavage agents; Introduction Small organic molecules able to bind DNA provide promises for
- experimental values are shown in Table 1. DNA binding studies Our previous DNA-binding studies with a series of amidoxime, ethanone oxime and aldoxime carboxylates as well as sulfonates of high, moderate or poor DNA photocleaving ability showed no substantial differences on the DNA affinities among the three
- identity. General procedures for the syntheses, as well as data and pictures of all spectra are provided in Supporting Information File 1. Interaction with CT DNA DNA-binding studies with UV–vis spectroscopy The binding constants of compounds 11 and 12 to CT DNA (Kb) were calculated by the Wolfe–Shimer
Two antibacterial and PPARα/γ-agonistic unsaturated keto fatty acids from a coral-associated actinomycete of the genus Micrococcus
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 297–304, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.29

- transfected with an expression plasmid containing the ligand-binding domain of human PPARα, -β/δ, and -γ fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (pPPARα–GAL4, pPPARδ–GAL4, or pPPARγ–GAL4, 0.25 µg), a luciferase reporter plasmid 17m2G TATA Luc (p17m2G, 1 µg), and the pSEAP-control vector (1 µg, Clontech, CA, USA
Reversible photoswitching of the DNA-binding properties of styrylquinolizinium derivatives through photochromic [2 + 2] cycloaddition and cycloreversion
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 111–124, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.13
- structural changes of the nucleic acid. In turn, both of these processes interfere with biologically relevant recognition processes between DNA and enzymes, e.g., topoisomerase [10]. Therefore, many potential lead structures of chemotherapeutic anticancer drugs exhibit DNA-binding properties [1][2][3][4][5
- ][6][7][8][9][10]. Nevertheless, most DNA-binding ligands have an insufficient selectivity towards the targeted nucleic acid, and they also accumulate in healthy tissue, so that the chemotherapeutic treatment of tumors with DNA-binding drugs still suffers from severe side effects because of the
- stilbene derivatives as photoswitchable DNA ligand [35], and in this case, the structure of the photoproduct was not fully identified. Also, it has been shown that a DNA-binding azoniatetracene may be generated by photoinduced [4 + 4] cycloreversion. However, this system was not applied for photoinduced
Photocontrolled DNA minor groove interactions of imidazole/pyrrole polyamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 60–70, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.8
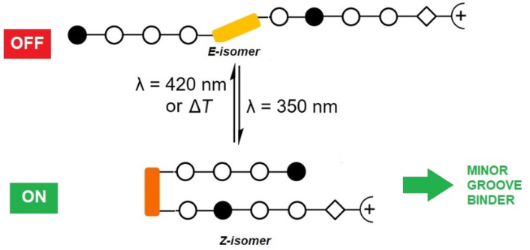
- switch in binding activity [29][30]. Importantly, it was demonstrated that the DNA binding was highly dependent on the linker length between the azobenzene and the distamycin moiety. Results and Discussion Here, we report on the design, synthesis, and characterization of photoswitchable minor groove
- ligand to examine the propensity of these derivatives to bind to DNA. The known intercalator thiazole orange (TO) was chosen as indicator because it exhibits an intense fluorescence band at 526 nm when bound to DNA, whereas it is only weakly fluorescent in solution. The displacement of TO from its DNA
- binding site was monitored by emission spectroscopy. The addition of 2.3 equiv of E-P1 led to a displacement of 50% of TO (cf. Supporting Information File 3), which indicates only a weak binding of E-P1 because as a groove binder, the latter occupies more binding sites than TO. These data indicate that E
Diversity-oriented synthesis of spirothiazolidinediones and their biological evaluation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2774–2781, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.269

- , phosphatidylserine molecules appear on the cell surface but the membrane is still impermeable for DNA-binding dyes (such as propidium iodide). The membrane integrity is lost at later stages of the cell death. Thus, while detecting the apoptosis, one can distinguish four types of cells: living cells (annexin V−/PI
Synthesis, biophysical properties, and RNase H activity of 6’-difluoro[4.3.0]bicyclo-DNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 79–88, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.9
- as the 6’F-bc4,3-DNA. Furthermore, duplexes of a 6’F-bc4,3-modified strand paired to RNA unveiled in the MD simulations a flexible minor groove distance [37]. This flexibility is thought to play a crucial role for the fitting of the duplex into the DNA-binding channel and the phosphate-binding pocket
Protein–protein interactions in bacteria: a promising and challenging avenue towards the discovery of new antibiotics
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2881–2896, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.267

- promisingly validating the sliding clamp as a feasible antibacterial target. Single-stranded DNA-binding protein (SSB) SSB is a class of proteins that coordinates fundamental cell processes including DNA replication, recombination and repair, and is, consequently, vital for cell survival. In addition, it also
Non-native autoinducer analogs capable of modulating the SdiA quorum sensing receptor in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2651–2664, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.243

- proteins consist of two domains: a larger N-terminal ligand-binding domain (LBD) connected to a smaller C-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD). In 2006, the structure of the EHEC SdiA LBD was solved by NMR in the presence and absence of AHL and demonstrated increased folding and structure upon ligand binding
Targeting the Pseudomonas quinolone signal quorum sensing system for the discovery of novel anti-infective pathoblockers
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2627–2645, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.241

- conformation of the PqsR-DNA binding domain, whereas the LBD is not affected extensively. Aryloxyacetindoles Spero Therapeutics further optimized M64 (42), firstly by changing the phenoxyphenylamide into a carbonyl-linked indole containing a hetarylether (43) [80]. Afterwards they varied the linkage of the
Microwave-assisted synthesis of biologically relevant steroidal 17-exo-pyrazol-5'-ones from a norpregnene precursor by a side-chain elongation/heterocyclization sequence
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2589–2596, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.236
- cancer selectivity. Since the molecular site of action of the tested compounds is not known, cisplatin (a clinically used DNA-binding anticancer agent) was applied as the reference. The results indicated that the 3β-acetates 6a–j exhibited weak or only modest antiproliferative activities, typically
Synthesis of 9-arylalkynyl- and 9-aryl-substituted benzo[b]quinolizinium derivatives by Palladium-mediated cross-coupling reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1871–1884, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.161
- ligands; fluorescence; heterocycles; Pd-mediated couling reactions; quinolizinium; Introduction Polycyclic cationic hetarenes are a paradigm of DNA-binding ligands whose association with the nucleic acid may affect the biological activities of the DNA [1][2][3][4]. For example, a DNA-bound heterocyclic
- ligand may interfere with DNA–enzyme recognition events, which are essential for DNA-based cellular processes, e.g., gene replication or transcription [1]. To this end, it was shown that DNA-binding ligands may operate as chemotherapeutic anticancer, antiviral or antibacterial drugs, for example as
- [14][15][16][17][18] and whose interaction with the nucleic acid may be used for fluorimetric detection of the latter [19][20]. To further exploit the DNA-binding properties of this specific class of cationic hetarenes, synthetic routes to novel derivatives with the desired substitution pattern and
Oligonucleotide analogues with cationic backbone linkages
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1293–1308, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.111
- relevance of enhanced nuclease stability and sequence-specific DNA binding. However, the gene-silencing effect could only be achieved if the modified oligonucleotide and the plasmid DNA were either mixed prior to cellular injection or if the oligonucleotide was injected first, pointing out a likely
- competition of the cationic antigene oligonucleotide with cellular histones for DNA binding [43]. Vasseur, Debart and co-workers have combined a variant of Letsinger's linkages with an α-configuration at the anomeric centers of antisense oligonucleotides [44][45]. They have found that such zwitterionic to




































































































































































































































































